Air quality alerts have been raging across the US this summer. If you live in a major metropolitan area, such as New York or San Francisco, you may already be aware of poor air quality from smog and other pollutants in the air. But did you know that bad air quality occurs all across the world, in rural areas, near mountains, and near forests? At Parcil Safety, we typically see a surge of respirator mask purchases during wildfire season, however no one has really answered the question “why should I wear a mask during poor air quality”?
What is the air quality index?
First, let’s talk about how you can measure poor air quality. Airnow.gov tracks the quality of air the United States and they actually have a search engine where you can you check the air quality for your area – check it out at https://www.airnow.gov/?city.
This will help you decide when it's necessary to stay indoors or wear a mask. Many mobile apps and weather platforms also provide AQI updates, so you can track changes throughout the day. For international users, check local environmental protection agencies or government health websites for similar services. Being informed can help you plan your activities accordingly, especially when there are high levels of pollutants in the air.
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a numerical scale used to measure and report the quality of outdoor air. It provides information about the level of air pollution and its potential impacts on human health. The AQI is often used by government agencies, environmental organizations, and health authorities to communicate air quality conditions to the public.
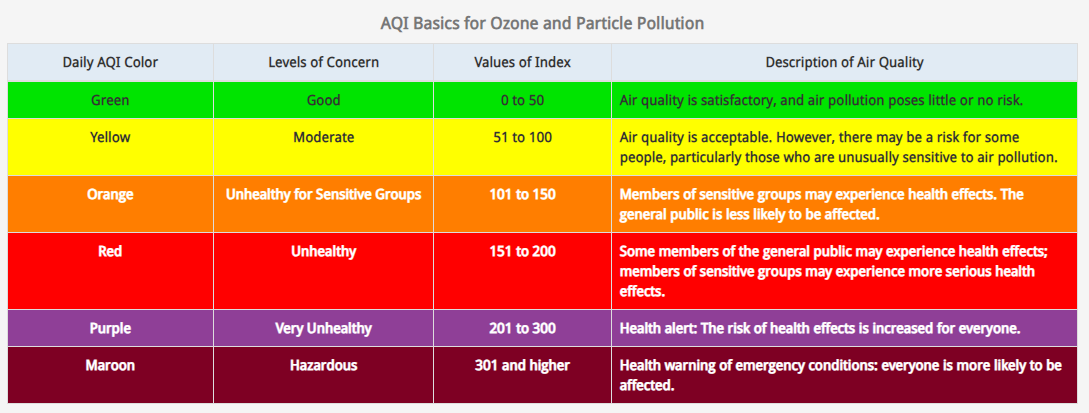
Airnow.gov also have a great chart (see below) using color coding to determining how toxic the air may be.

When is air quality dangerous?
So, when is air quality considered to be “dangerous”?
The AQI typically measures several common air pollutants, including particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and carbon monoxide (CO). Each pollutant is assigned a specific index value based on its concentration in the air.
The scale of the AQI varies from country to country, but it is commonly categorized into six levels, each corresponding to a different level of air quality and potential health effects. These levels are often color-coded to provide a quick visual indication of air quality:
Good (Green): Indicates minimal or no health risks associated with air quality.
Moderate (Yellow): Indicates acceptable air quality but may pose a moderate health concern for sensitive individuals.
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups (Orange): Indicates that some individuals, such as children, the elderly, or those with respiratory conditions, may experience health effects.
Unhealthy (Red): Indicates that the general population may experience adverse health effects, while sensitive individuals may experience more serious effects.
Very Unhealthy (Purple): Indicates a higher risk of serious health effects for the entire population.
Hazardous (Maroon): Indicates the highest level of air pollution, posing a severe health risk to all individuals.
The AQI is often updated in real-time or on a daily basis, allowing people to stay informed about current air quality conditions and make decisions accordingly, such as adjusting outdoor activities or taking preventive measures like wearing masks when necessary.
Air quality and environmental responsibility
Beyond personal protection, understanding air quality and taking steps to reduce pollution is an essential part of environmental responsibility.
Poor air quality is often a result of human activity, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, deforestation, and waste. By making conscious decisions to reduce our carbon footprint, we can help improve air quality for ourselves and future generations.
For example, reducing car usage by carpooling, biking, or using public transport helps cut down on vehicle emissions. Supporting green energy initiatives, such as wind or solar power, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to air pollution.
Also, planting trees can improve local air quality, as trees naturally absorb pollutants and release oxygen. Advocating for better regulations on air quality standards can also push governments and industries toward cleaner practices.
Collectively, these actions not only help reduce pollution but also contribute to the health and well-being of communities, creating a cleaner, healthier environment. It’s essential to take both personal precautions and active steps toward environmental sustainability to address the broader issue of poor air quality.
What is the best mask to wear during bad air quality
You may be considering buying disposable N95 masks for protecting your lungs against poor air quality, but the best masks you can get would be an actual reusable respirator mask.
Reusable respirator masks typically come with enhanced filtration such as P3 filtration, dual activated filters to help protect from chemicals in the air as well as particulates, have tighter seal and a more secure fit which minimizes the potential for unfiltered air to enter around the edges of the mask, and since they are reusable, you can get extended duration of use – that is, you can keep the respirator with you in case of an emergency situation (such as wildfire smoke), and typically you can replace the filters without having to dispose of the respirator itself.
Parcil Safety’s best two options for poor air quality is the PD-100 Full Face Respirator and the T-60 Half Face respirator. The PD-100 offers full-face protection, covering both the respiratory system and eyes, which is ideal for environments with high levels of contaminants or hazardous materials. It provides a more secure seal and better protection against smoke, chemicals, and particulates. On the other hand, the T-60 Half Face Respirator covers only the nose and mouth, offering a more lightweight and breathable option for situations where full face protection is not required. Both masks are effective, but the choice depends on the level of exposure and comfort needed.
Tips for using masks effectively during poor air quality
Wearing a mask can provide significant protection during poor air quality conditions, but it’s important to use it correctly to ensure maximum effectiveness.
First, ensure that the mask fits tightly over your nose and mouth, with no gaps along the sides. This ensures that harmful particles cannot bypass the filter and enter your lungs. If you're using a reusable respirator mask, replace the filters as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain the mask's effectiveness.
Also, avoid wearing masks that are too loose or made from materials that don't provide proper filtration, as these will not offer sufficient protection. For people with respiratory conditions, such as asthma, it’s important to monitor your symptoms and consult with a healthcare provider if air quality worsens.
Lastly, consider wearing a mask when the AQI reaches levels that are categorized as "Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups" or worse.
What situations may create poor air quality?
Wearing a mask for air quality concerns depends on the specific pollutants present and their concentration levels. Here are some general guidelines for wearing masks based on different air quality conditions:
• Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Pollution: PM2.5 refers to tiny particles suspended in the air that can be inhaled into the lungs. If the air quality index (AQI) indicates high levels of PM2.5 (typically above 150), wearing a mask, such as an N95 or P100 respirator, can provide some protection.
• Smoke and Wildfire Conditions: During periods of intense smoke caused by wildfires or other sources, it is recommended to wear masks, particularly those with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter. N95 masks or masks specifically designed for smoke protection can be effective in reducing the inhalation of harmful particles. Check out article on best masks for wildfire smoke.
• Industrial Pollution: In areas with high levels of industrial pollution, such as near factories or industrial zones, wearing masks can help reduce exposure to hazardous gases, fumes, and particulate matter. Masks with appropriate filters, such as N95 masks, can be beneficial.
• Allergens: If you have allergies to airborne substances like pollen, dust mites, or animal dander, wearing a mask can help reduce exposure to these allergens, especially during peak allergy seasons.
• Pandemic Situations: During the COVID-19 pandemic or any other infectious disease outbreaks, wearing masks can help prevent the transmission of respiratory droplets and protect both the wearer and others. In such cases, surgical masks, N95 respirators, or masks recommended by health authorities are typically used.
• Agricultural Spraying: If you are seeing planes, drones or UAVs spraying in fields near where you live, you may want to be prepared to wear a respirator or gas mask. Many times, chemicals being sprayed by these aircrafts may be harmful if you breathe them in. Check out our article on the recent drones sightings and whether you should be concerned here.
The health impacts of poor air quality
Exposure to poor air quality, especially over long periods, can have significant health consequences.
Particulate matter (PM2.5), which includes fine particles from sources like wildfire smoke, vehicle emissions, and industrial pollution, can deeply affect respiratory and cardiovascular health. These particles can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing inflammation, worsening asthma, bronchitis, and other chronic respiratory conditions. Long-term exposure may even increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
In addition to respiratory issues, poor air quality can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, leading to discomfort and even more severe health problems.
People with pre-existing conditions such as lung disease, heart disease, or diabetes are at greater risk. Children and the elderly are also particularly vulnerable due to their weaker immune systems and respiratory functions.
Wearing a mask during high-pollution periods, especially if you live in areas with frequent air quality alerts, can help mitigate these health risks. It's also essential to limit outdoor activities, particularly strenuous exercises, when air quality is poor to avoid further strain on the body.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of masks can vary depending on the type of mask, its fit, and the specific pollutants involved. For optimal protection, it is advisable to refer to local air quality guidelines and recommendations provided by health authorities in your region.
If you have any questions or concerns, please don’t hesitate to send us an email at service@parcilsafety.com or give us a call at +1 855 715 1400. We are always here to help!
Stay safe and stay protected!




















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.